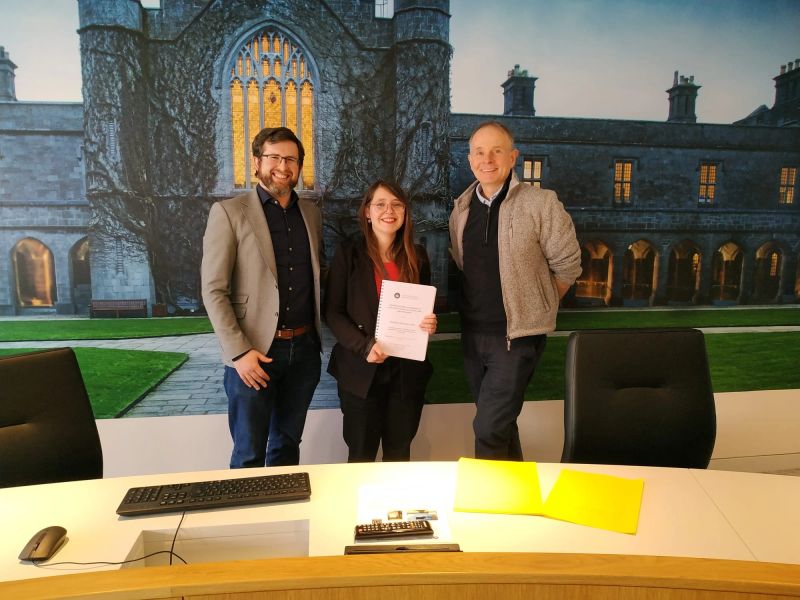
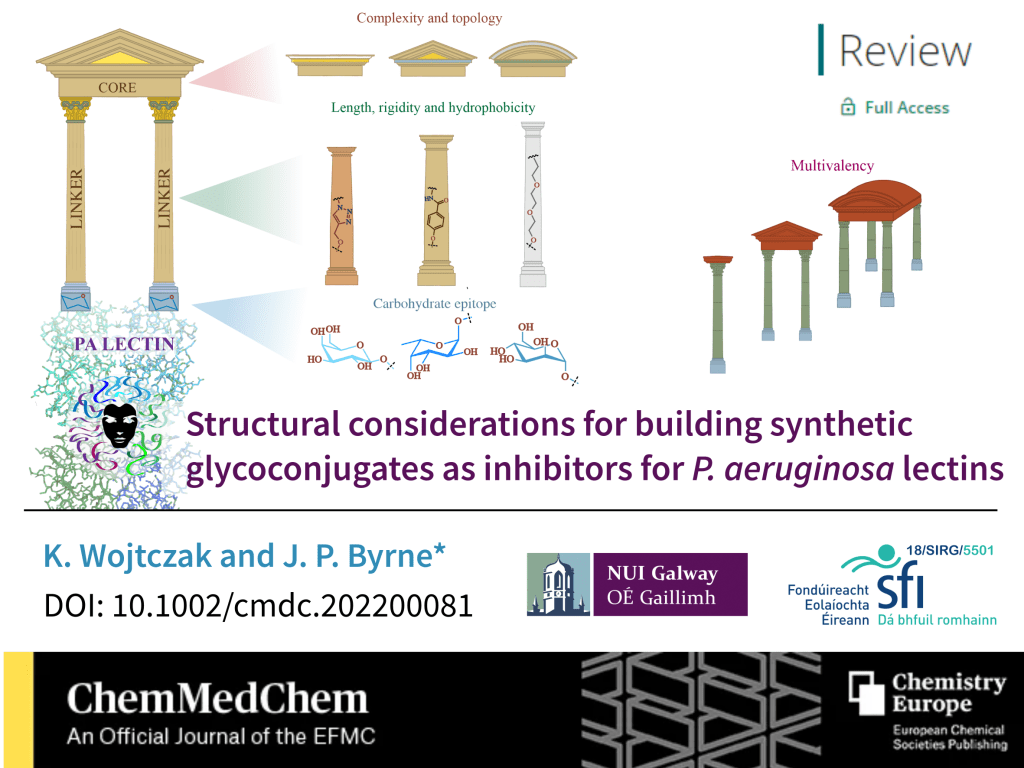
Very proud of my very first PhD student Karolina Wojtczak who successfully defended her thesis last Thursday. A lot of hard work has paid off and she has left the group lots of interesting starting points for future projects (in addition to a few more imminent publications). Her thesis was titled “Metal-based glycoconjugates as molecular sensors for lectins and anti-adhesives”.
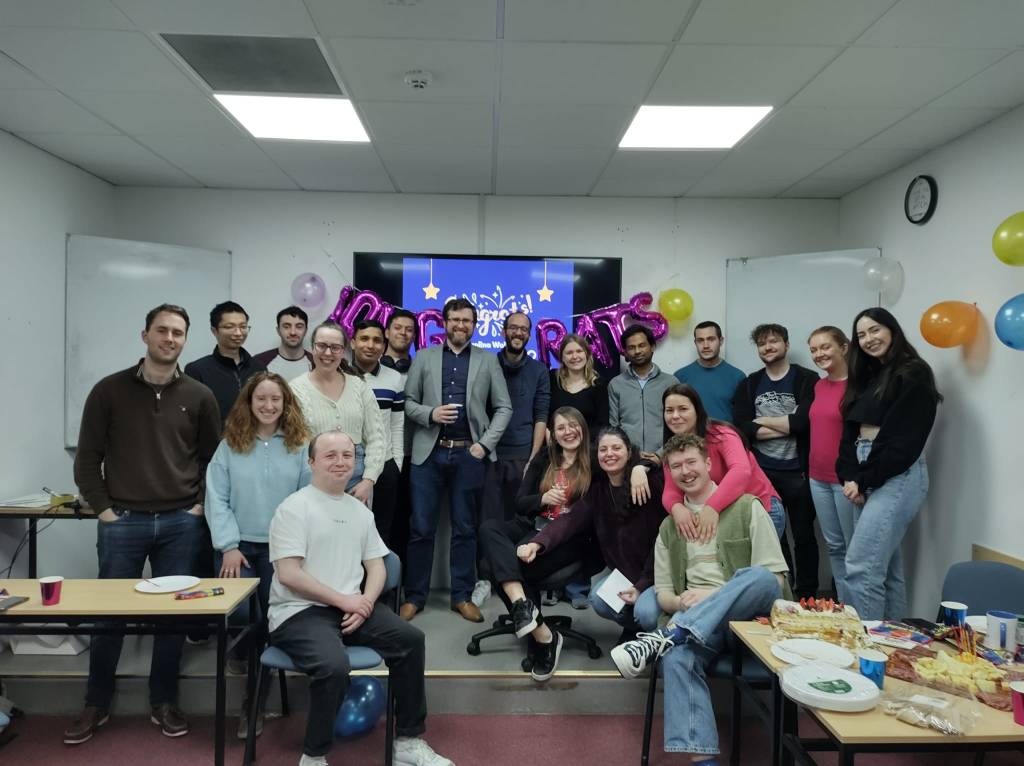
Karol was an absolute pleasure to have in my lab and I wish her all the best with her bright future. I’m sure she will achieve great things. Congratulations!
A great celebration was had in Galway to mark the occasion.
Thanks to Research Ireland (formerly SFI) (18/SIRG/5501) for financial support and Paul Murphy for co-supervising her, particularly after I moved to UCD last year.
Karol has already started a position as a Development Chemist in Sterling Pharma Solutions.